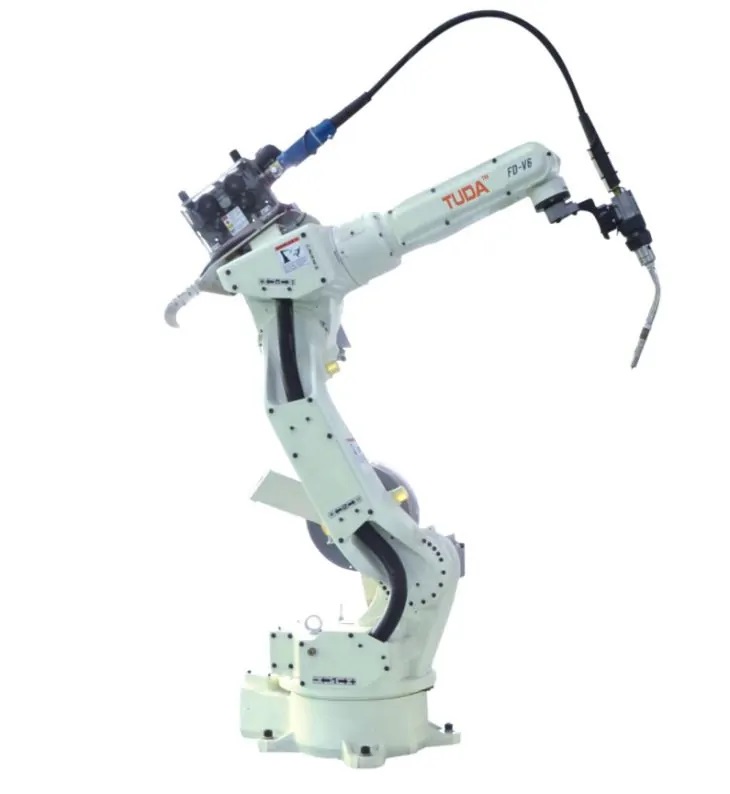
What is a welding robot?
What is a welding robot?
Welding robots are industrial robots that perform welding (including cutting and spraying). According to the definition of a standard welding robot by the International Organization for Standardization (ISO), an industrial robot is a multi-purpose, reprogrammable automatic control manipulator (Manipulator) with three or more programmable axes for field of industrial automation. In order to adapt to different uses, the mechanical interface of the last axis of the robot is usually a connecting flange, which can be connected to different tools or end effectors. The welding robot is to install welding tongs or welding (cutting) guns on the end flange of the industrial robot, so that it can be welded, cut or thermally sprayed.
With the development of electronic technology, computer technology, numerical control and robot technology, the automatic welding robot has been used in production since the 1960s, and its technology has become increasingly mature, with the following advantages:
1) Stabilize and improve the welding quality, which can reflect the welding quality in the form of numerical values;
2) Improve labor productivity;
3) Improve the labor intensity of workers, and can work in harmful environments;
4) Reduced the requirements for workers' operating skills;
5) Shorten the preparation period for product modification and replacement, and reduce the corresponding equipment investment.
Therefore, it has been widely used in all walks of life.
Welding robots mainly include two parts: robots and welding equipment. The robot consists of the robot body and the control cabinet (hardware and software). The welding equipment, taking arc welding and spot welding as an example, consists of welding power source, (including its control system), wire feeder (arc welding), welding gun (clamp) and other parts. For intelligent robots, there should also be sensing systems, such as laser or camera sensors and their control devices.
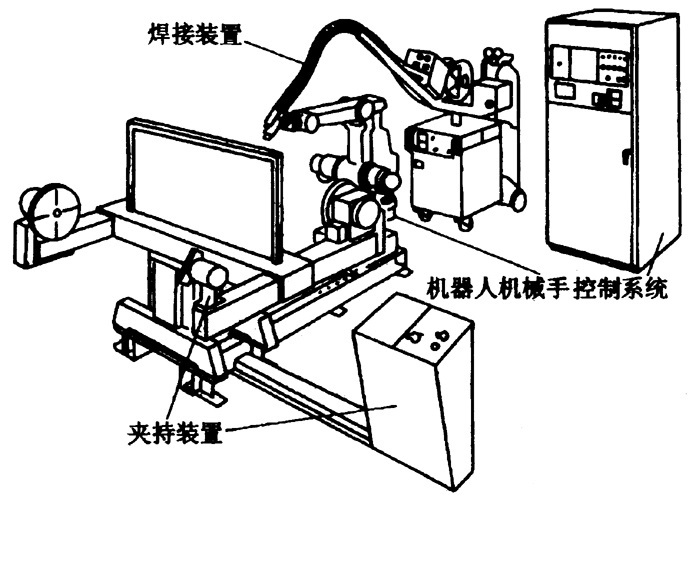
Schematic diagram of welding robot
The welding robots produced in various countries in the world are basically joint robots, and most of them have 6 axes. Among them, the 1, 2, and 3 axes can send the end tool to different spatial positions, while the 4, 5, and 6 axes solve the different requirements of the tool attitude. The mechanical structure of the welding robot body mainly has two forms: one is a parallelogram structure, and the other is a side-mounted (pendulum) structure. The main advantage of the side-mounted (swinging) structure is that the upper and lower arms have a large range of motion, so that the working space of the robot can almost reach a sphere. Therefore, this robot can work upside down on the rack to save floor space and facilitate the flow of objects on the ground. However, this side-mounted robot has a cantilever structure on the 2 and 3 axes, which reduces the rigidity of the robot and is generally suitable for robots with small loads for arc welding, cutting or spraying. The upper arm of the parallelogram robot is driven by a pull rod. The pull rod and the lower arm form two sides of a parallelogram. Hence the name. The early developed parallelogram robots have a relatively small workspace (limited to the front of the robot), making it difficult to work upside down. However, the new parallelogram robot (parallel robot) developed since the late 1980s has been able to expand the working space to the top, back and bottom of the robot without the stiffness problem of the measuring robot, so it has received widespread attention. This structure is suitable not only for light but also for heavy robots. In recent years, robots for spot welding (with a load of 100-150kg) mostly use robots with a parallelogram structure.
Each axis of the above two robots is for rotary motion, so the servo motor is driven by the cycloidal pinwheel (RV) reducer (1-3 axis) and harmonic reducer (1-6 axis). Before the mid-1980s, DC servo motors were used for electrically driven robots, but since the late 1980s, countries have switched to AC servo motors. Because the AC motor has no carbon brushes and has good dynamic characteristics, the new robot not only has a low accident rate, but also greatly increases the maintenance-free time, and the acceleration (decreasing) speed is also fast. Some new light robots with a load of less than 16kg have a maximum movement speed of the tool center point (TCP) of more than 3m/s, accurate positioning and low vibration. At the same time, the control cabinet of the robot also uses a 32-bit microcomputer and a new algorithm, so that it has the function of optimizing the path by itself, and the running trajectory is closer to the teaching trajectory.
High work efficiency. How much load capacity a spot welding robot needs to have depends on the type of welding tongs used. For the welding tongs separated from the transformer, a robot with a load of 30 to 45 kg is sufficient. However, on the one hand, due to the long secondary cable, this kind of welding tongs has large power loss, which is not conducive to the robot extending the welding tongs into the workpiece for welding; on the other hand, the cable keeps swinging with the movement of the robot, and the cable is damaged quickly . Therefore, the use of integrated welding guns is gradually increasing. The mass of this welding gun together with the transformer is about 70kg. Considering that the robot must have enough load capacity, it can send the welding tongs to the spatial position for welding with a large acceleration, and generally choose a heavy-duty robot with a load of 100-150kg. In order to meet the requirements of short distance and rapid displacement of welding tongs during continuous spot welding. The new heavy-duty robot adds the ability to complete a 50mm displacement in 0.3s. This puts forward higher requirements for the performance of the motor, the computing speed and the algorithm of the microcomputer.






